The Basics of Type
Typography could be considered the most important part of any design. It’s definitely among the most important elements of any design project. And yet it’s often the part of a design that’s left for last, or barely considered at all. Designers are often intimidated by typography, which can result in bland typographical design or a designer always using one or two “reliable” typefaces in their designs.
This series aims to change that. If you’re intimidated by typography, or even just aren’t quite sure where to start, then read on. We’ll break down typographic theory and practice, starting with the basics (so that everyone starts on the same page).
In this part, we’ll talk about the basics of typographic theory, including the different kinds of typefaces (and how typefaces and fonts differ), as well as the basic anatomy of a typeface. And each part will also offer more resources for delving deeper into typography.
Typefaces vs. Fonts: Difference?
A lot of people use the terms “typeface” and “font” interchangeably. But they’re two very distinct things. Before we get started talking about typography, let’s get our terms straight.
A typeface is a set of typographical symbols and characters. It’s the letters, numbers, and other characters that let us put words on paper (or screen). A font, on the other hand, is traditionally defined as a complete character set within a typeface, often of a particular size and style. Fonts are also specific computer files that contain all the characters and glyphs within a typeface.
Several types of fonts are;
- Old style serif
- Transitional serif
- Square sans-serif
- Geometric sans-serif
- Formal script
- Casual script
When most of us talk about “fonts”, we’re really talking about typefaces, or type families (which are groups of typefaces with related designs).
Typography is, in essence, the art and technique of arranging type. It's central to the skills of a designer and is about much more than making the words legible. Your choice of typeface and how you it works with your layout, grid, colour scheme and so on will make the difference between a good, bad and great design.
There's a lot of jargon in the discipline of typography – covering everything from the correct names for the different parts of your letterforms to the terms relating to how you arrange them within a design. In this article, we present a comprehensive glossary of typography terms. Jump to page 2 to take a look. On this page, we'll cover the basics you need to know to get started working with type.

01. Font selection
 There is a vast selection of typefaces for you to choose from
There is a vast selection of typefaces for you to choose from
Font design is a long and involved process. Typefaces are created by craftspeople over a substantial period of time, using talent honed over many years. The best, professionally designed fonts come with various weights and styles to form a complete family, plus carefully considered kerning pairs, multi-language support with international characters and expressive alternate glyphs to add character and variety to typesetting.
So while there's an astonishing array of free fonts to choose from online, you'll need to check the one you choose includes all the options you need to create a great design.
Even within the paid-for options, so much choice can be overwhelming. It can be tempting to stick to the classics. If you want to branch out and are in need of some inspiration, take a look at these inspired alternatives to Helvetica, or explore these perfect font pairings.
02. Size
All typefaces are not created equal. Some are fat and wide; some are thin and narrow. So words set in different typefaces can take up a very different amount of space on the page.
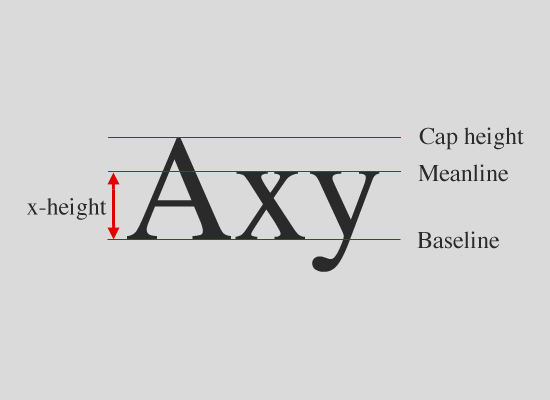
The height of each character is known as its 'x-height' (quite simply because it's based on the 'x' character). When pairing different typefaces, it's generally wise to use those that share a similar x-height.
The width of each character is known as the 'set width'. This spans the body of the letter, plus the space that acts as a buffer between one letterform and the next.
The most common method used to measure type is the point system, which dates back to the 18th century. One point is 1/72 inch. 12 points make one pica, a unit used to measure column widths. Type sizes can also be measured in inches, millimetres, or pixels.
03. Leading
Leading describes the vertical space between each line of type. It's so named because, in the days of metal typesetting, strips of lead were used to separate lines of type. For legible body text that's comfortable to read, a general rule is that your leading value should be anything between 1.25 and 1.5 times greater than the font size.
04. Tracking and kerning
Kerning is the process of adjusting the space between characters to create a harmonious pairing. For example, where an uppercase 'A' meets an uppercase 'V', their diagonal strokes are usually kerned so that the top left of the 'V' sits above the bottom right of the 'A'.
Kerning is similar to tracking, but they are not the same thing. Tracking is the process of adjusting the spacing of all characters in a word, and is applied evenly.
05. Measure
The term 'measure' describes the width of a text block. If you're seeking to achieve the optimum reading experience, it's clearly an important consideration. If your lines are too long, your reader can easily get lost, while a too-short measure breaks up the reading experience unnecessarily.
There are a number of theories to help you define the ideal measure for your typography. One rule of thumb is that your lines should be 2-3 alphabets in length (so 52-78 characters, including spaces).
06. Hierarchy and scale
If all the type within a layout looks the same, it's difficult to know which is the most important information. Size is one key way in which typographers create hierarchy and guide their readers. Headings are usually large, sub-headings are smaller, and body type is smaller still.
Size is not the only way to define hierarchy – it can also be achieved with colour, spacing and weight.
Note: To know more about Typography download all the resourses mentioned below.