Fundamentals of Computer
📘 Contents
- 💡 Introduction to Computers
- 🧩 Classification of Computers
- 📚 Generations of Computers
- 🧠 Computer Memory
- 🔢 Number System
- 🛠️ Computer Hardware
- 📦 Computer Software
- ⌨️ Input & Output Devices
- 💾 Storage Devices
- ⚙️ Operating System Basics
- 🌐 Introduction to Computer Networking
- 🌍 Internet Basics
- 🔐 Cyber Safety & Best Practices
- 🖥️ Practical Computer Applications
- 🔮 Quantum Computers
- 🤖 Artificial Intelligence: Use Cases and Importance
1. Introduction to Computers
A computer is an electronic device that accepts input, processes data, stores information, and provides output in a useful format. It performs tasks with speed, accuracy, and automation. Basic components of a computer system include hardware (physical parts), software (programs), data, and users.
Key Characteristics:
- Speed: Performs millions of operations per second
- Accuracy: High precision with minimal errors
- Automation: Operates automatically once programmed
- Versatility: Can perform a variety of tasks
- Storage: Stores large amounts of data
Applications:
Education, Business, Healthcare, Banking, Government, Entertainment
2. Classification of Computers
Computers can be classified based on size, purpose, and type:
By Size:
- Microcomputers: Personal computers (desktops/laptops)
- Minicomputers: Multi-user systems
- Mainframes: Large systems for high-volume data
- Supercomputers: High-speed for scientific calculations
By Purpose:
- General-Purpose: Word processing, browsing, gaming
- Special-Purpose: Embedded systems like ATMs
By Type:
- Analog: Measures physical values
- Digital: Works with binary data
- Hybrid: Combines analog and digital features
3. Generations of Computers
Computer evolution is categorized into generations:
- First Generation (1940-1956): Vacuum tubes, slow, large (e.g., ENIAC, EDVAC, UNIVAC, IBM-701, and IBM-650)
- Second Generation (1956-1963): Transistors, smaller, faster (e.g., IBM 1401)
- Third Generation (1964-1971): Integrated Circuits (ICs), more reliable
- Fourth Generation (1971-Present): Microprocessors, personal computers
- Fifth Generation (Present & Beyond): Artificial Intelligence, robotics
Computer evolution is categorized into generations:
First Generation (1940-1956)
Key Characteristics:
- Used vacuum tubes
- Very large in size
- Consumed a lot of electricity
- Produced a lot of heat
- Programming in machine language
Examples:
ENIAC: The Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer, one of the earliest general-purpose electronic computers, used 18,000 vacuum tubes.
EDVAC: The Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer was a stored-program computer designed by John von Neumann.
UNIVAC: The Universal Automatic Computer was one of the first mass-produced computers.
IBM-701: IBM's first commercially available computer, used for scientific and military applications.
IBM-650: One of the first mass-produced computers, used for scientific and business calculations.
Second Generation (1956-1963)
Key Characteristics:
- Used transistors instead of vacuum tubes
- Smaller, faster, and more reliable
- Less heat production
- Programming in assembly language
Examples:
IBM 1401
CDC 1604
Third Generation (1964-1971)
Key Characteristics:
- Used Integrated Circuits (ICs)
- Smaller and more efficient
- Lower cost
- Used high-level programming languages
Examples:
IBM System/360
PDP-8
Fourth Generation (1971-Present)
Key Characteristics:
- Used microprocessors
- Introduction of personal computers (PCs)
- Very compact and fast
- Used GUI-based operating systems
Examples:
IBM PC
Apple Macintosh
Fifth Generation (Present & Beyond)
Key Characteristics:
- Based on Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Voice recognition and natural language processing
- Expert systems and robotics
- Focus on parallel processing
Examples:
AI-based systems like IBM Watson
Robots, smart assistants (Alexa, Siri)
4. Computer Memory
Memory stores data temporarily or permanently.
Primary Memory:
- RAM (Random Access Memory): Volatile, temporary storage
- ROM (Read Only Memory): Non-volatile, permanent instructions
Secondary Storage:
- Hard Disk, SSD, USB Drive, Optical Discs
- Cache Memory: Fast memory between CPU and RAM
- Registers: Smallest memory in the CPU used during processing
5. Number System
Computers use various number systems to represent data.
- Decimal (Base 10): 0-9
- Binary (Base 2): 0 and 1
- Octal (Base 8): 0-7
- Hexadecimal (Base 16): 0-9 and A-F
Conversions: Binary to Decimal, Decimal to Binary, etc.
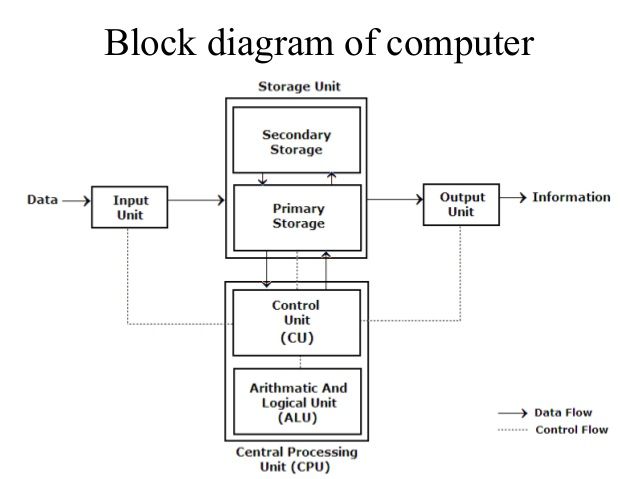
6. Computer Hardware
Hardware includes all physical components:
- Input Devices: Keyboard, Mouse, Scanner
- Output Devices: Monitor, Printer
- CPU (Central Processing Unit): ALU + CU + Registers
- Motherboard: Connects all components
- Memory Units: RAM, ROM
7. Computer Software
Software is a set of instructions.
Types:
- System Software: Operating system, device drivers
- Application Software: MS Office, Browsers
- Programming Software: IDEs, Compilers
8. Input & Output Devices
Input Devices: Used to give data to the computer
- Keyboard, Mouse, Joystick, Scanner, Webcam
Output Devices: Used to get data from the computer
- Monitor, Printer, Speaker, Projector
9. Storage Devices
Storage devices hold data.
- Magnetic Storage: Hard Disk, Floppy
- Optical Storage: CD, DVD
- Solid State Storage: SSD, USB Drive
- Cloud Storage: Google Drive, Dropbox
10. Operating System Basics
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware, software, and resources.
Functions:
- File management
- Process management
- Memory management
- Device control
Types:
- Single-user, Multi-user
- GUI (Graphical), CLI (Command Line)
- Examples: Windows, Linux, macOS, Android
11. Computer Networking
Networking connects computers to share data.
Types:
- LAN (Local Area Network): Small areas like office
- MAN (Metropolitan Area Network): City-wide
- WAN (Wide Area Network): Large scale like the internet
Devices: Router, Switch, Hub, Modem
12. Internet Basics
The internet is a global network of computers.
Terms:
- WWW (World Wide Web): Collection of web pages
- Browser: Software to access web (Chrome, Firefox)
- URL: Address of a website
- Email: Electronic messaging
- Cloud Computing: Using remote servers for storage and software
13. Cyber Safety & Best Practices
Cyber safety involves protecting yourself online.
Tips:
- Use strong passwords
- Avoid clicking unknown links
- Install antivirus software
- Use secure websites (HTTPS)
- Be aware of phishing and scams
14. Practical Computer Applications
Hands-on practice is essential:
- Windows OS navigation
- MS Word: Typing, formatting
- MS Excel: Tables, charts, formulas
- MS PowerPoint: Slides, transitions
- Paint & Notepad
- Internet Browsing & Email Setup
15. Quantum Computers
Quantum computers use principles of quantum mechanics for data processing.
Key Concepts:
- Qubit: Basic unit of quantum information; can be 0, 1, or both simultaneously
- Superposition: A qubit can represent multiple states at once
- Entanglement: Qubits can be linked so the state of one affects the other
- Quantum Speed-up: Capable of solving complex problems faster than classical computers
Applications:
- Drug discovery
- Cryptography
- Weather forecasting
- Financial modeling
Example Quantum Systems:
- IBM Quantum
- Google Sycamore
- D-Wave Systems
Limitations (Current):
- Very expensive
- Sensitive to noise
- Require ultra-low temperatures
Quantum computing is still in its early stages but has the potential to revolutionize technology and computation.
16. Artificial Intelligence: Use Cases and Importance
Artificial Intelligence (AI) enables machines to mimic human intelligence to perform tasks.
Importance of AI:
- Enhances productivity through automation
- Improves decision-making with data analysis
- Enables smart and interactive user experiences
Key Use Cases:
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Chatbots, voice assistants
- Image Recognition: Medical imaging, security
- Recommendation Systems: Shopping, streaming platforms
- Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving technology
- Predictive Analytics: Business forecasting, stock analysis
Popular AI Tools/Platforms:
- ChatGPT (by OpenAI): Conversational AI, education, content writing, coding help
- Grok (by xAI): AI chatbot integrated with X (Twitter), personalized responses
- Gemini (by Google): Multimodal AI for productivity, content generation
- DeepSeek: Search-enhanced AI with programming and reasoning capabilities
Ethical Considerations:
- Data privacy
- Job displacement
- Bias in AI algorithms
AI is transforming all sectors, from education and healthcare to business and entertainment, making it essential knowledge for future readiness.